Atrial Fibrillation will double in 8 years!
Arrhythmia Has Different “Types”
A-Fib is a “Type” of Arrhythmia
Atrial-Fibrillation (arrhythmia) is the most common type. It’s an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart. A-fib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. The number of Americans that have it is 6.1 million and Atrial Fibrillation will double in 8 years to 12 million by 2030. What are the causes of Atrial Fibrillation?
Understanding that A-Fib has different types of Arrhythmias such as, Paroxysmal, Persistent, Long Term Persistent and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation helps you to understand what category you’re in and which type you have. You must understand how your heart works when you have A-Fib
. Atrial Fibrillation is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. Instead of the sinus node that directs the electrical rhythm, many different impulses rapidly fire at once, causing a very fast and chaotic rhythm in the atria. Because the electrical impulses are so fast and chaotic, the atria cannot contract and or squeeze blood effectively into the ventricle.
Atrial Fibrillation can decrease the heart’s pumping ability. The irregularity can make the heart work less efficiently. In addition, A-Fib that occurs over a long period of time can significantly weaken the heart and lead to heart failure. It is associated with an increased risk of stroke, heart failure and death. So, what are the causes of Atrial Fibrillation?
Here are some causes,

- The major cause for the AF is damaged heart’s electrical system and other causes include:
- Family history
- Abnormal or damaged structure of the heart either at birth or during the lifetime
- Improper functioning of the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinus node
- High blood pressure
- Heart attacks
- Coronary heart disease or disease of blood vessels of the heart
- Abnormal heart valves
- Metabolic disorders such as overactive thyroid gland, diabetes
- Exposure to stimulants including certain medications and tobacco
- Previous heart surgeries
- Stress
- Sleep apnea or sleep disorders
- Lung and kidney diseases
- Viral infections
- Obesity
- Alcohol consumption
- Risk factors include:
- Age – older the age higher the risk
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Heart diseases
- Alcohol consumption
- Obesity
-
Hereditary
What are the Dangers?
-
Clearly the biggest danger is an increased risk of Stroke because the atria are beating rapidly and irregularly, blood does not flow through them as quickly. This makes the blood more likely to clot. If a clot is pumped out of the heart, it can travel to the brain, resulting in a stroke or to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
-
Atrial Fibrillation is directly related to Stroke.
-
A-Fib may be related to alcohol or excessive caffeine use, stress, certain drugs, electrolyte or metabolic imbalances, severe infections, or genetic factors. In some cases, no cause can be found. The risk of A-Fib increases with age, particularly over age 60.
Some Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
-
Heart Palpitations- sudden pounding, fluttering or racing sensation of the heart
-
Lack of Energy-Feeling over-tired
-
Dizziness-light-headed or faint
-
Shortness of Breath-Having difficulty breathing
How is This Disease Treated?
The goals of treatment for atrial fibrillation include regaining a normal heart rhythm (sinus rhythm), controlling the heart rate, preventing blood clots and reducing the risk of stroke.
Many options are available to treat atrial fibrillation, including lifestyle changes, medications, catheter-based procedures and surgery. The type of treatment that is recommended for you is based on your heart rhythm and symptoms.
Medication Therapy

Antiarrhythmic medications help return the heart to its normal sinus rhythm or maintain normal sinus rhythm.
Some rhythm control medications may actually cause more arrhythmias, so it is important to talk to your doctor about your symptoms and any changes in your condition.
Rate Control medications
Beta blockers like metoprolol, atenolol are used to help slow the heart rate during atrial fibrillation. These medications do not control the heart rhythm but do prevent the ventricles from beating too rapidly. If you are taking warfarin alternatives, regular blood tests are not required. Talk to your doctor about the anticoagulant medication that is right for you.
Change your lifestyle
It’s recommended that you keep a log of activities that trigger episodes.
Quit smoking, Limit Alcohol, caffeine, energy drinks, tea, and colas. Just use your better judgement, you will know what works for you and what doesn’t.
Procedures
When medications do not work to correct or control atrial fibrillation, or when medications are not tolerated, a procedure may be necessary to treat the abnormal heart rhythm, such as: electrical cardioversion, pulmonary vein antrum isolation procedure, ablation of the AV node followed by pacemaker placement, or surgical ablation.
An option your doctor may consider is Excision of the LAA
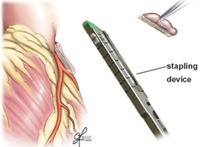
If a patient has atrial fibrillation and requires surgery to treat other heart problems (such as valve disease or coronary artery disease), the surgeon may perform the surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation at the same time.
Excision or exclusion of the left atrial appendage: During surgical procedures to treat atrial fibrillation, the left atrial appendage is removed, and the tissue is closed with a special stapling device, or it can be excluded with a device called the Atri-Clip. The Atri-Clip is implanted from outside the heart and stops the blood flow between the LAA and left atrium.
Pacemaker option
A pacemaker is a device that sends small electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain a suitable heart rate. Pacemakers are implanted in people with AF who have a slow heart rate. The pacemaker has a pulse generator (that houses the battery and a tiny computer) and leads (wires) that send impulses from the pulse generator to the heart muscle, as well as sense the heart’s electrical activity.
Another option is the Watchman
The watchman device is inserted into the LAA and allows you to get off of blood thinner forever,for more information, call 1-844-294-3320 or go to the Watchman.
Or Contact;
Cleveland Clinic heart specialist, or call the Miller Family Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Resource & Information Nurse at 216.445.9288 or toll-free at 866.289.6911. They’d be happy to help you.
If you’d like to leave a comment, feel free, for more information on A-Fib go toAtrial Fibrillation Awareness – Troubleshooting A-Fib (shers-shop-site.com)
All the Best, Sherry
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.
